In the modern dynamic Corporate Software Inspector digital environment organizations have been compelled to deal with a new challenge of ensuring secure, compliant and effective software environments. A corporate software inspector is an important defense measure that offers complete view and container on the software environment of an organization. This is such a great tool, which is inseparable to IT administrators, security experts, and compliance officers who are required to ensure their enterprise software infrastructure is secure and well-managed.
So what is a Corporate Software Inspector?
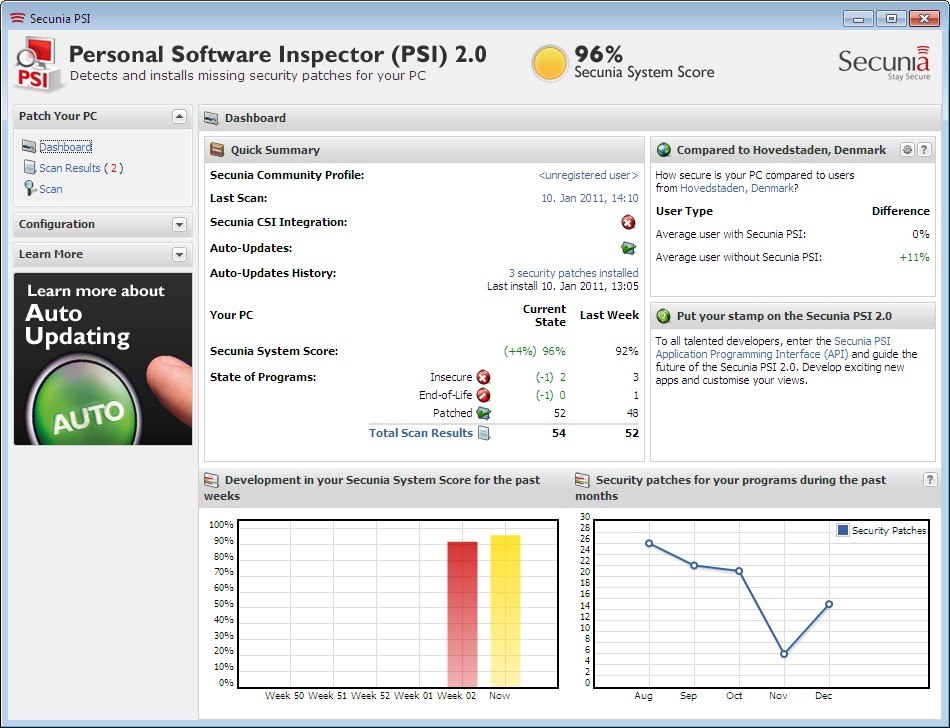
The corporate software inspector is a highly focused security and management system which can be used to scan, examine and monitor software programs on the complete network infrastructure of an organization. These advanced software offer visibility at real-time to installations, vulnerability, licensing and software security patch status of multiple endpoints, servers and platforms.
Corporate software inspector has the main role of beyond the software inventory. It is an all in one platform comprising vulnerability scanning, both patching and compliance monitoring as well as security testing functions. The tools help organizations handle a secure software environment without breaking any regulations and maximizing the level of operational efficiency.
The contemporary corporate software inspectors tend to work via agent-based examination, agentless network tracing, and central control consoles. The multi-layer strategy guarantees maximum coverage of a wide variety of IT environments, including the traditional on-premises infrastructure and up to the cloud-based deployments with hybrid implementations.
Important Characteristics and Functions
End-to-end Software Discovery and Inventory
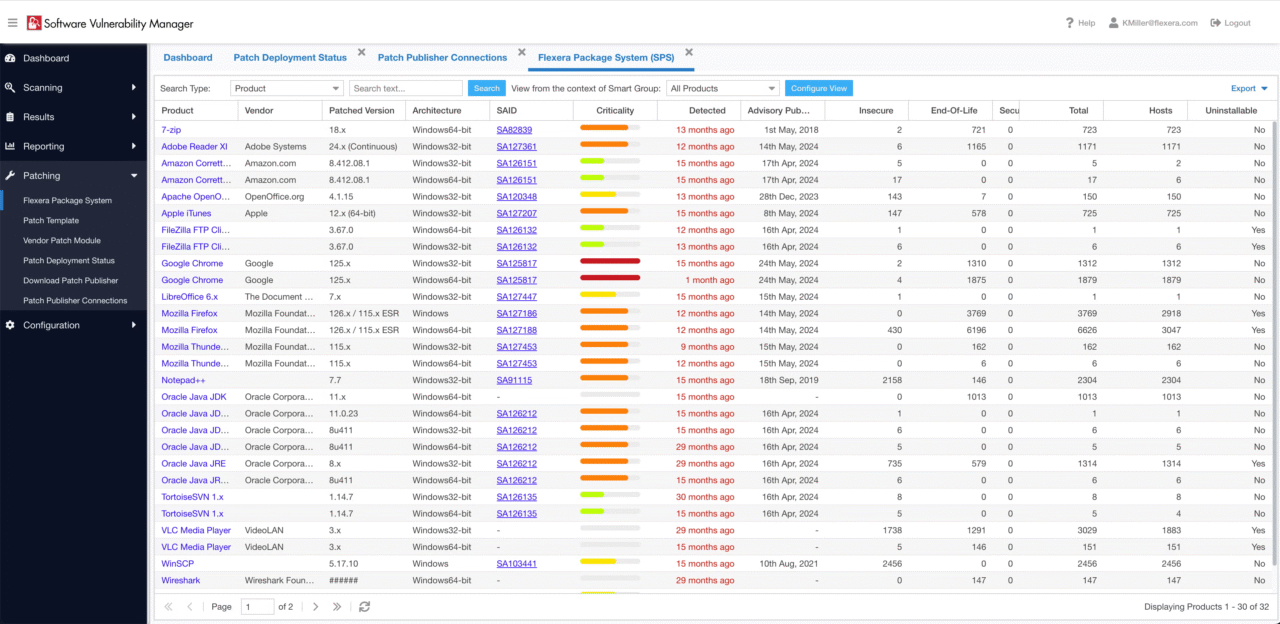
To have a strong Corporate Software Inspector watchdog is an inspector of software that gives you automatic discovery in locating all the software that is installed in any network of an organization. These are commercial usage, open-source software, user-developed programs, and system utilities Corporate Software Inspector. The discovery process works in real-time mode, and any new installations and modifications will be discovered at once and recorded.
Inventory function entails detailed databases with information about software versions, date of installation Corporate Software Inspector, usage and license information. This secure thorough visibility helps organizations to make the appropriate decisions on software standardization, software license optimization and security measures.
Risk Management and Vulnerability Assessment
The detection of security vulnerability in the installed software would be one of the most important roles of a software inspector in a corporate environment Corporate Software Inspector. Such products have comprehensive databases of known vulnerabilities which are updated constantly with the newest threat intelligence of security researchers and vendors.
The vulnerability assessment practice usually consists of installing software version comparison with known vulnerability databases, ranking risks according to priority based on their severity and exploitability potential, and delivering at-least recommendations of what is to be done to remediate the situation Corporate Software Inspector. State of the art systems are combined with Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) specifications in order to facilitate unified risk calculations.
Integration of Patch Management
Powerful corporate software inspection elements are able to join the current patching presentations, such as Microsoft windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM). With this integration, automated processes of patch deployment that may be configured in accordance with the policies of the organization and levels of risk tolerance, become possible.
The patch management controls do not just work on the operating system but also incorporates third-party application patches, which provides 100 percent coverage of the security of the entire software stack Corporate Software Inspector. Testing and staging is possible in many systems to approve the patches before they are deployed into production.
Monitoring and Reporting Compliance
There are large numbers of regulations that modern organizations have to adhere to as well as regulations within the industry and inside the organizations Corporate Software Inspector. A software auditor within the corporate is equipped with overall tools of monitoring compliance, they keep a record of software being installed against sanctioned application lists, license agreements, and regulatory standards.
The reporting module creates elaborate compliance report, which is appropriate during audits, management overview and applications to regulatory authorities Corporate Software Inspector. Such reports usually contain inventory of software, vulnerability assessment, patch status reports, and compliance gap reports.
Learning Styles and Best Practices
Planning, preparation.
Effective usage of software inspector in a corporation should be planned and prepared well Corporate Software Inspector. The first step that organizations can take to implement the process of monitoring their IT infrastructure is by performing a full assessment of the infrastructure used by the organization, all the systems, platforms, and environments that need to be monitored must be captured in the assessment process.
Development of Security policies, compliance, and operation procedure that will govern the configuration and working of the inspector should be laid out in the planning stage. This also involves setting vulnerability assessment policies Corporate Software Inspector, patch management procedures and reporting policies.
Deployment and Configuration
Installation of management servers, endpoint configuration of chemical agent software, and setting up network scanning capabilities to perform agentless discovery are the common and standard techniques used during the deployment process Corporate Software Inspector. An organization is supposed to perform this in phases, where there is a pilot deployment in a controlled manner that is followed by a production system.
Configuration requirements involve the specification of the scanning schedules, parameters of vulnerability assessment and integration with the existing security and management tools settings Corporate Software Inspector. The right configuration achieves this performance and has the least effect on the network resources as well as on the performance of the system.
Constant Management and Optimisation
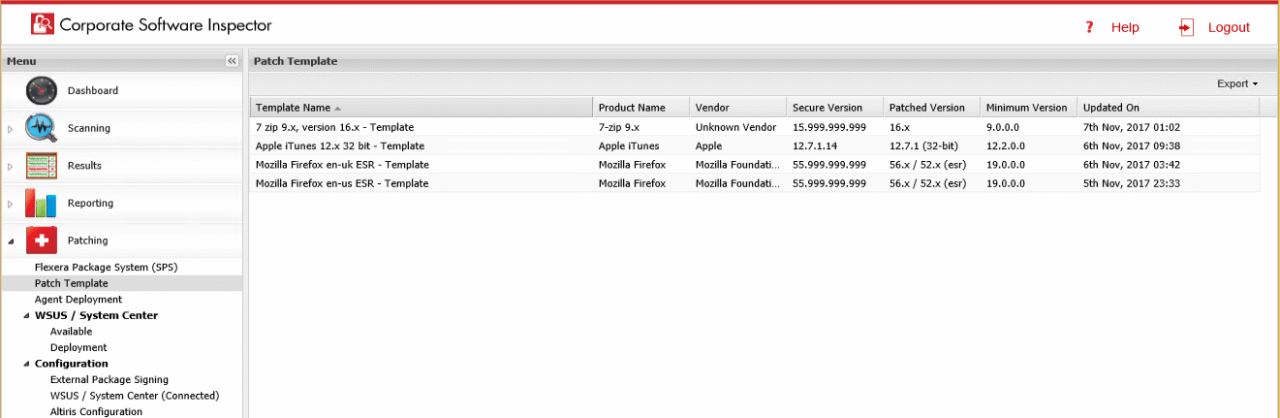
Active work of a corporate software inspector presupposes constant management and optimization. It consists of an update of vulnerability databases and refinement of scanning parameters and constant tracking of the performance of the system and its effectiveness.
Organization should develop and practice frequent review procedures to determine and make corrections on the effectiveness of the tool, gaps to be addressed, and adherence to the changing security needs and business goals Corporate Software Inspector. This will involve periodic evaluation on coverage, accuracy and interoperability with other security instruments.
Return on Investment, Advantages
Increased Security Posture
Enhanced security posture is the most important advantage of the given corporate software inspector implementation. These tools can assist organizations in minimizing the size of their attack surface and the likelyhood of being breached by ensuring complete visibility of the software vulnerabilities present in an organization, and allowing the rapid deployment of software patches.
The positive detection of vulnerabilities helps organizations deal with security problems before they could be exploited by the malicious actors Corporate Software Inspector. This is a proactive method that is much more economical than the reactive incident response and recovery activities.
Operational Efficiency
Corporate software inspectors simplify several run-of-the-mill IT monitoring functions, cutting the amount of hand labor displayed in software inventory Corporate Software Inspector, vulnerability analysis, and patch regulation. This automation allows IT tasks to dedicate more time on other valuable tasks whilst maintaining a high level of security management that is consistent and holistic.
The centralized management tools offer centralised visibility of complex, distributed IT environment, so that various tools and manual work are removed Corporate Software Inspector. This merges out the complexity in running operations thereby enhancing efficiency.
Risk Management and Compliance
Corporate software inspectors help organizations that are under regulated to comply because of their compliance monitoring and reporting capabilities. The compliance with a range of regulations and standards can be proved with the help of these tools which gives the required visibility and documentation Corporate Software Inspector.
The risk management features allow the organization to make competent software decision-making, investments in security, or where to run their operations Corporate Software Inspector. This data-based strategy to risk management enhances resources distribution and choices made.
Perspectives and New Trends
The development of corporate software inspectors is fast becoming an even faster process, with the emergence of new technologies and the adaptation of new security conditions Corporate Software Inspector. DevOps practices, containerization, and cloud-native architectures change the way organizations deploy and manage software and new inspection and monitoring methods are needed.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence technology is also incorporated to corporate software inspectors to achieve better vulnerability detection results, automating threat analysis, and better predictive analytics Corporate Software Inspector. Such developments will enhance software security management in terms of effectiveness/efficiency as well.
It is advisable that organizations have a way of rating these trends and incorporating the corporate software inspector solutions that they take into consideration since it is important to make sure that the solutions selected are capable of adjusting itself to changing needs and technologies.
(FAQs) About Corporate Software Inspector
Q1 What are the differences between the corporate software inspector and traditional antivirus software?
Antivirus software will concentrate on detection and removal of malware whereas corporate software inspector will give detailed insight to every software installation, detect vulnerability, and deploy patch. It is an active tool of security management, but not a threat surveillance system.
Q2 How long does it take the average implementation of a corporate software inspector?
The implementation projects can be more or less long depending on the size of an organization and its complexity, and they can take between 4-12 weeks. This involves planning, implementations, customization, testing and trainings of the staff. Usually, pilot deployments may be achieved within 2-4 weeks.
Q3 Is it possible to use cloud-based applications and services with corporate software inspectors?
Contemporary software inspectors on corporations have a cloud-native functionality and are capable of examining a cloud-native application, SaaS setting, and hybrid environments. Nevertheless, this might not be complete in terms of the cloud services offered and access privileges.
Q4 What are the most common metrics that organizations will follow upon using a corporate software inspector?
The relevant measures are the rates of new vulnerabilities being discovered, the success of implementing patches, the levels of compliance, the time needed to address vulnerabilities that are of high-priority and the inventory of the software generated. These measures assist to evaluate the effectiveness of the tool and the ROI.
Q5 What is done with the false positives of the vulnerability detection by corporate software inspectors?
Good corporate software testers put advanced filtering and validation technologies in place in order to reduce the number of false positives. They generally supply a contextual information, risk scoring, and validation to enable the administrators to determine and prioritize real security problems and block false alarms.
You May Also Read